
The use of hard forks in cryptoasset networks is a one-of-a-kind method of resolving disagreements over planned protocol improvements. In the event that a party within a cryptocurrency’s community disagrees with the majority of network members, they have the option of forking the code and operating their own „private“ chain.
In the case of Bitcoin (BTC) and its various forks, many of which appeared to exist just to piggyback on Bitcoin’s brand in order to profit its inventors, this is exactly what happened.
Let’s take a look at some of the most well-known Bitcoin forks and evaluate how they have fared in comparison to the original cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) is a cryptocurrency that was created in August 2017 by a faction within the Bitcoin community that was dissatisfied with the Bitcoin scaling roadmap and the implementation of the SegWit upgrade.
The new blockchain, dubbed Bitcoin Cash, was created by miners and developers who sought to overcome Bitcoin’s scaling limits, which resulted in slow transaction times and high transaction fees, by allowing larger blocks to be mined and distributed.
Those who are opposed to larger blocks (as was the majority of the Bitcoin community) argue that doing so will lead to centralization, because as the size of the blockchain grows, it will become increasingly difficult for individuals to run nodes on their own.
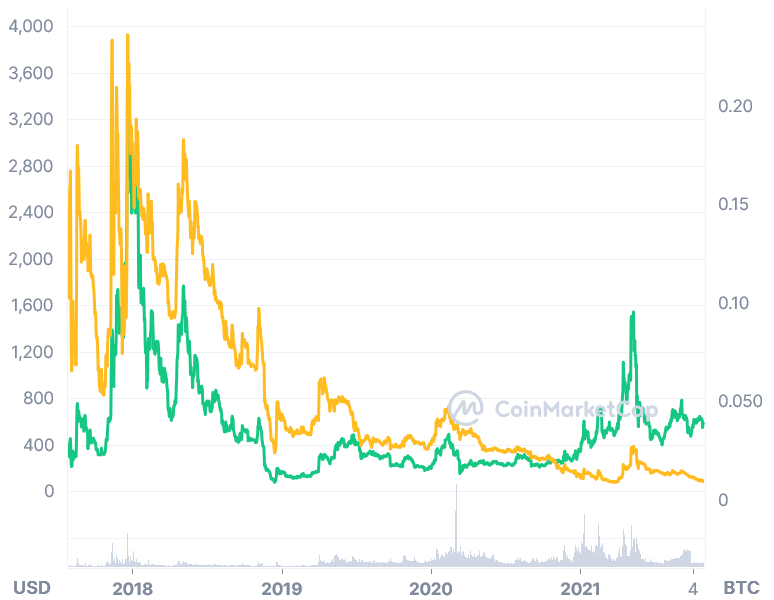
BCH began trading at approximately USD 400 in mid-2017, before surging to more than USD 600 a month later.
When the price of bitcoin crossed the USD 20,000 threshold in December 2017, the price of bitcoin cash reached a high of more than USD 3,000. While writing, the price of Bitcoin Cash was trading in the USD 600’s range.
BCH, on the other hand, has been losing value in relation to the price of bitcoin since the beginning of 2018. Despite the fact that its dollar value remains relatively high, the price of BCH has fallen to an all-time low in relation to Bitcoin, trading below 0.001 BTC.
Bitcoin SV (BSV)
Bitcoin SV (BSV), a fork of a fork, was created in November 2018 as a hard fork of the Bitcoin Cash cryptocurrency. Craig S. Wright and Calvin Ayre led a group of Bitcoin Cash (BCH) community members in their argument that BCH’s features were insufficiently significant to meet the conditions for properly scaling the Bitcoin Cash blockchain.
Furthermore, proponents of BSV were strongly in favor of returning to the original Bitcoin design, as represented by Bitcoin version 0.1, as opposed to any other design. Bitcoin SV refers to the Bitcoin whitepaper under the appellation ‚Satoshi Vision,‘ which did not advocate for second-layer, off-chain scaling options, as the source of its name.
When it comes to the technical details, BSV was created with a default block size of 128 MB, which was eventually increased to 2 GB in a subsequent upgrade. As a strategy to encourage miners to continue mining new blocks after block rewards have expired, the new structure was designed to process more transactions while also producing more transaction fees in order to generate more transaction fees.
Craig S. Wright, the leader of Bitcoin SV, continues to assert that he is Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin, despite the fact that he has failed to provide proof to support his claim.
Because Wright’s assertion is critical to BSV’s raison d’être, his failure to provide evidence to support his claim has had a negative impact on the altcoin’s price.
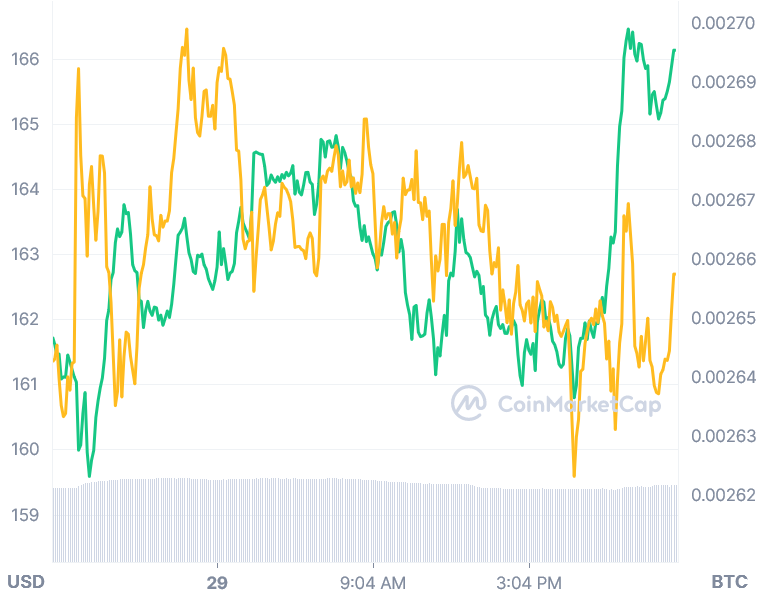
When BSV first went public in November 2018, it was trading at approximately USD 112 per share. Bitcoin was trading at above USD 6,000 at the time of writing. BSV rose to an all-time high of USD 441 in April 2021, following in the footsteps of the rest of the cryptocurrency markets that were on the rise at the time. BSV is currently trading at USD 170 per unit at the time of writing.
However, when compared to the price of bitcoin, the value of BSV has plummeted, reaching a low of 0.00277 BTC in October, following a long-term slide that began in early 2020.
Bitcoin Gold (BTG)
Bitcoin Gold (BTG) is a cryptocurrency that was launched in October 2017 with the tagline „restore bitcoin’s decentralized nature.“
Jack Liao and his other co-founders hoped to do this by creating a version of Bitcoin that could be mined using graphics processing units (GPUs) that anyone could run from their homes. They argued that mining had become too complex and expensive for consumers to mine Bitcoin using their personal computers, and as a result, they chose a proof-of-work algorithm called Equihash BTG that was optimized for GPU mining.
BTG was successful in establishing itself as a popular coin among at-home miners, but it was unable to build any other important use cases outside of that.
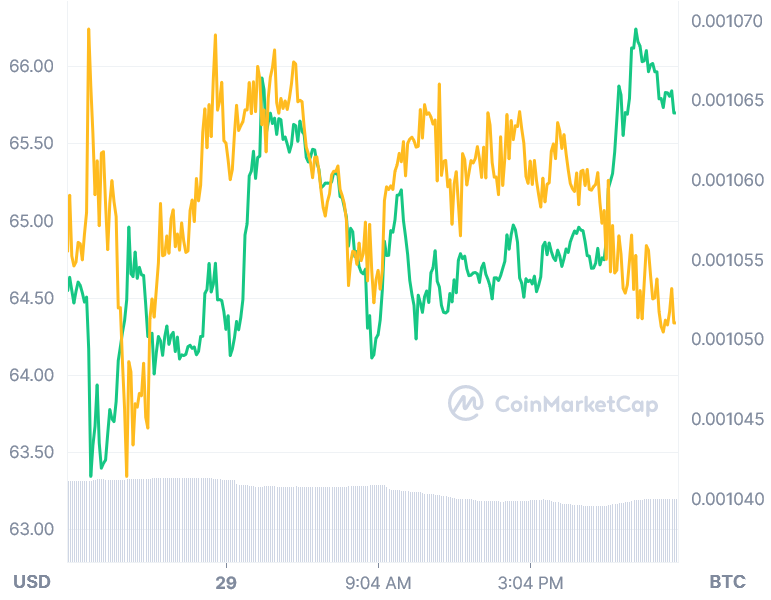
Bitcoin Gold (BTG) made its market debut in October 2017 at USD 137 and surged in November to hit an all-time high of nearly USD 400. However, the price of BTG would collapse to below USD 100 in 2018 and continue its downward trajectory as the market grew concerned about the cryptocurrency’s perceived vulnerability to hackers, which was underlined by the 51 percent of attacks it had endured that year.
Unexpectedly, the price of BTG has plummeted in relation to the value of bitcoin, with the coin currently trading at less than 0.0012 BTC at the time of writing.
Bitcoin Diamond (BCD)
The Bitcoin Diamond (BCD) fork took place in November 2017, during a time when Bitcoin forks were suddenly popular among cryptocurrency enthusiasts. In order to improve the Bitcoin protocol, the BCD founders developed their chain with the (cl)aim of speeding up transaction times, decreasing transaction fees, and increasing anonymity.
They created a new proof-of-work consensus method intended to deter network attacks, as well as separated transaction signatures from on-chain transactions in order to boost capacity and enable a higher on-chain transaction throughput per second on the Ethereum blockchain.
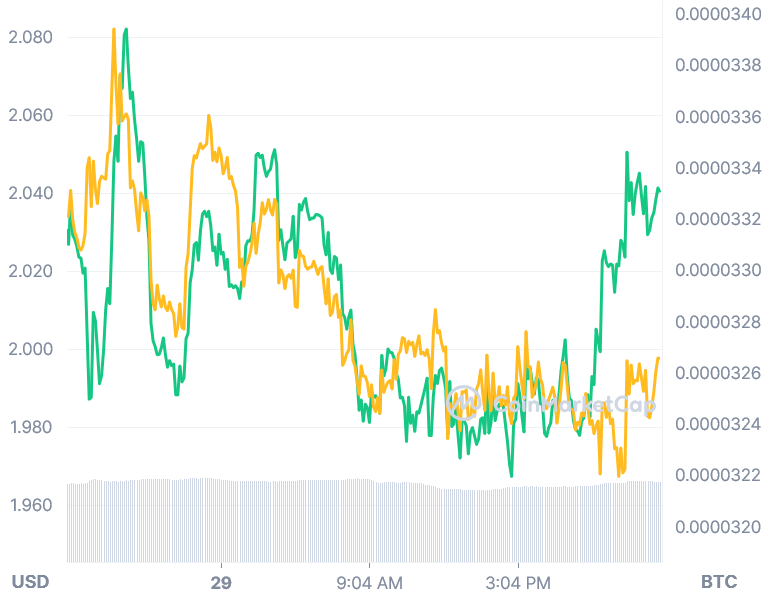
In November 2017, the price of Bitcoin Diamond soared to more than USD 66 per coin. It did not endure, as the price began to fall in January 2018, down to USD 5 on the fifth of that month. The price of BCD is now USD 2.31 at the time of writing.
When measured against the price of bitcoin, the value of BCD plummeted almost immediately after it was introduced. BCD is currently trading for less than 0.00001 BTC per coin at the time of writing.
Bitcoin Private (BTCP)
Bitcoin Private (BTCP) was founded in March 2018 as a result of a hard fork between Bitcoin and Zclassic (ZCL). The formation of Bitcoin Private was motivated by the desire to combine the privacy features of Zclassic with the security of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Bitcoin Private was not a regular fork, but rather a ‚fork merge,‘ which involved forking away from the Bitcoin protocol and merging it with the Zclassic cryptocurrency.
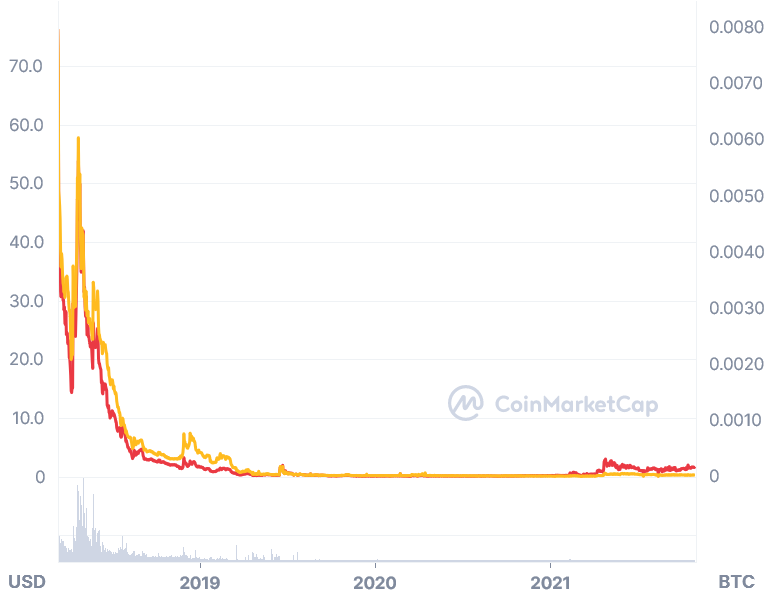
BTCP was introduced at a price of USD 68 in early March 2018. However, this price level was short-lived, and the price fell as low as USD 15 in April before eventually falling as low as USD 2 in November, when the market finally crashed. Since then, the price of BTCP has been unable to recover its previous levels.
When compared to the value of bitcoin, the BTCP coin fell below 0.00003 BTC per coin.
Get Forked!
When it comes to Bitcoin forks, the lesson is very straightforward: any cryptocurrency that bears the name Bitcoin but isn’t actually Bitcoin will lose value in comparison to the real thing in the long run.
If you’re looking for Bitcoin forks that claim to be the „genuine Bitcoin,“ you won’t find them since the market has determined they aren’t. Bitcoin is the only thing that is Bitcoin.























