Ether (ETH) entered the July session with perhaps the most bullish outlook, with a key technical update dubbed EIP-1559 promising to increase the scarcity of its native token ETH via the network’s first-ever burning mechanism.
However, so far this month, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization has lagged significantly behind leader Bitcoin.
The positive correlation became apparent on July 13, following the New York opening bell, when Ether fell below $2,000 to a two-week low, in lockstep with Bitcoin, which fell below $32,500.
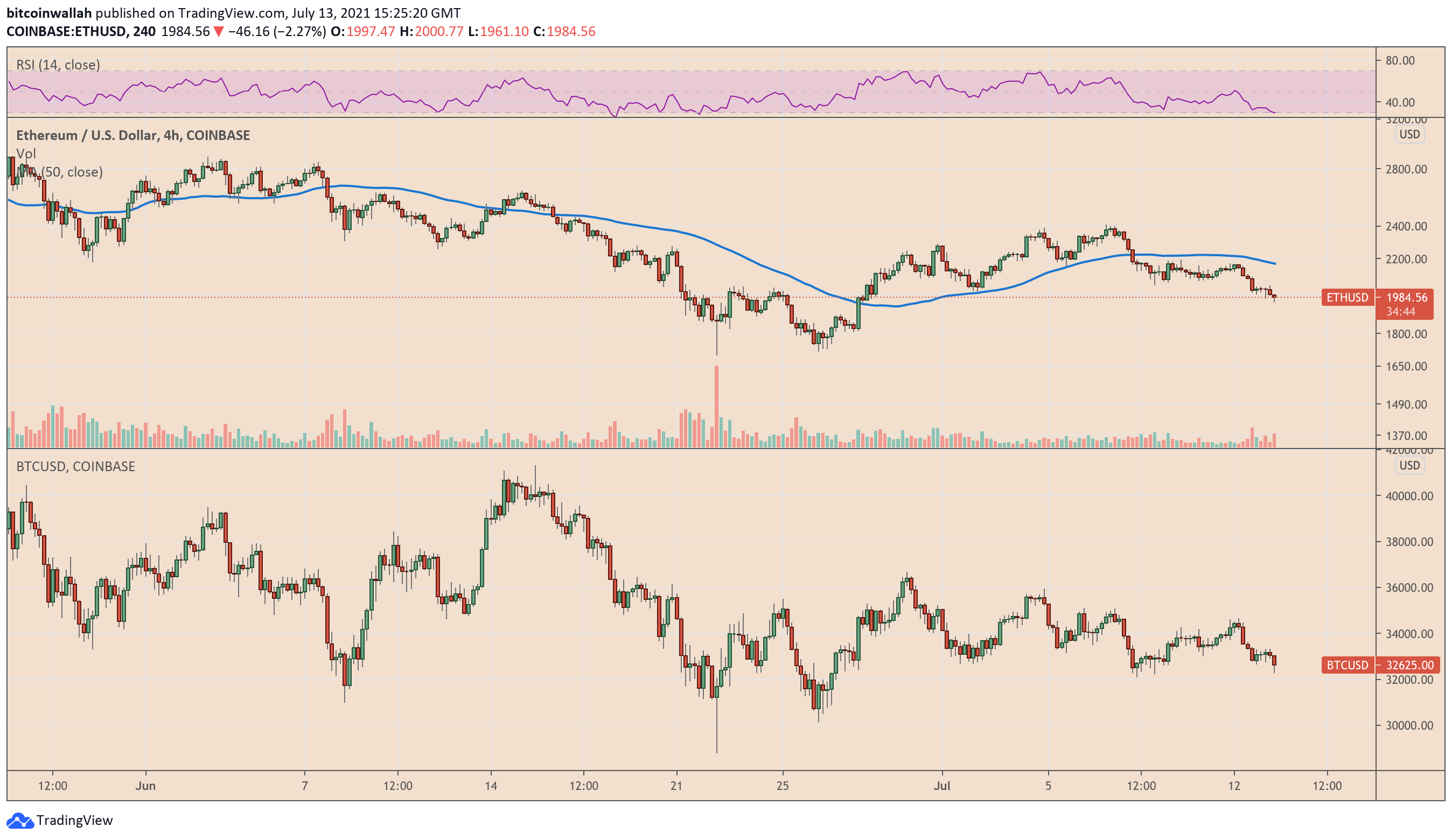
As it happened, the ETH/USD exchange rate fell 3.43 percent to an intraday low of $1,961.10.
The pair’s modestly bearish move was in lockstep with Bitcoin’s apprehensive decline following the release of the latest US inflation data.
The consumer price index in the United States increased by 0.9 percent in June to 5.4 percent year over year, its highest level since 1991.
Traders dumped Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies in response to the news, citing concerns that a persistently rising inflation rate would prompt the US Federal Reserve to end its quantitative easing policies.
Macro inflation vs. Ethereum deflation
In detail, the minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee’s June meeting revealed that officials were in favor of at least two rate hikes by the end of 2023, assuming inflation stays above their 2% target.
Since March 2020, the central bank has kept interest rates below 0.25 percent, reducing investor demand for dollars and increasing demand for so-called safe-haven assets such as Bitcoin.
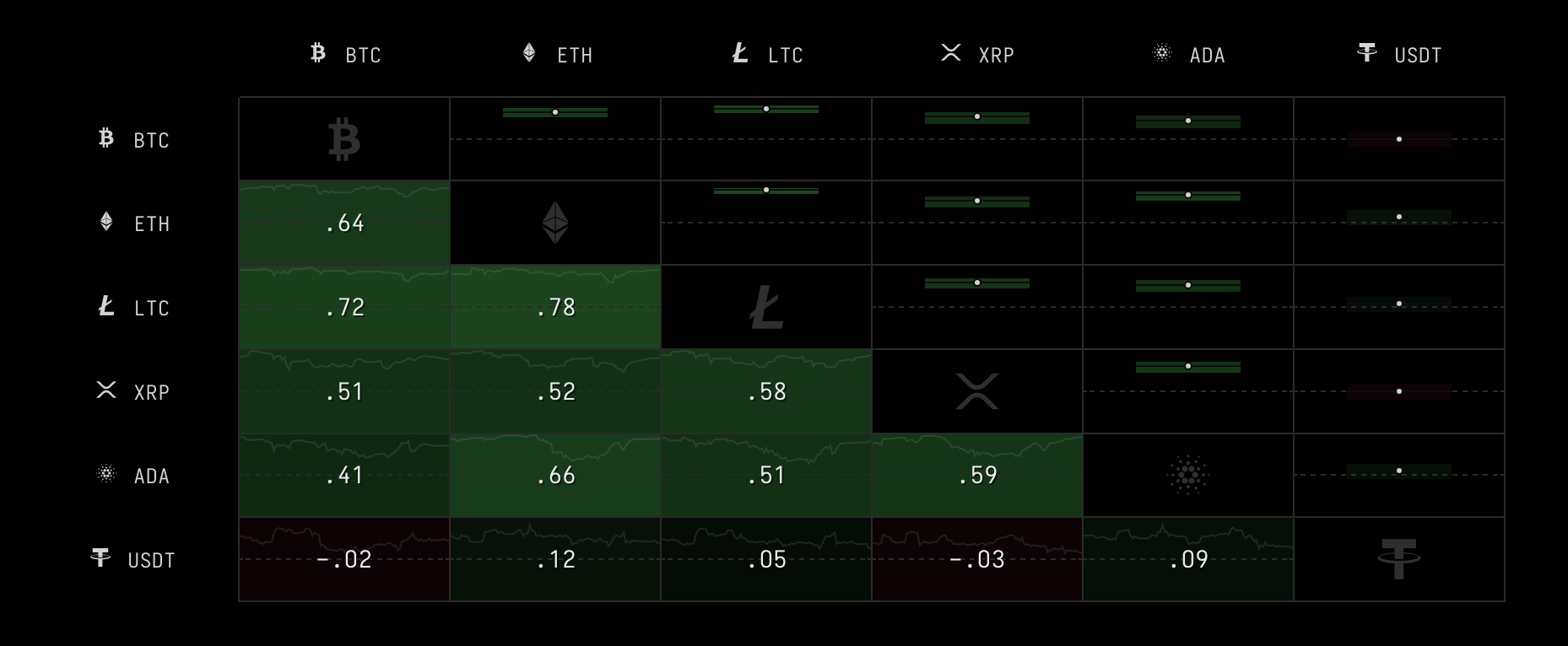
Ether, which has a one-year correlation coefficient of 0.64 with Bitcoin, surged throughout 2020 and the first quarter of 2021 on similar macroeconomic fundamentals.
However, the cryptocurrency outperformed Bitcoin, owing to its involvement in a slew of burgeoning crypto sectors, including decentralized finance (DeFi), nonfungible tokens (NFT), and stablecoins.
However, the Ethereum network encountered technical difficulties in the form of congested bandwidth.
Miners—entities that process and add transactions to Ethereum’s public ledger—increased their fees in response to the overloaded blockchain.
In some instances, users were required to pay more in gas fees than the amount transferred.
The issues appear to have been resolved definitively, as Ethereum intends to migrate from a miner-friendly but energy-intensive proof-of-work protocol to a faster and cheaper proof-of-stake protocol.
In detail, the so-called London hard fork aims to address those inefficiencies through the inclusion of five improvement proposals.
One of the enhancement protocols, EIP-1559, introduces a new fee structure that reduces the inflationary nature of Ether.
It proposes to burn a portion of the fee collected in ETH, thereby putting the cryptocurrency under deflationary pressure.
Additionally, the upgrade eliminates the need for miners in favor of validators.
Ethereum does this by requiring each validator to secure at least 32 ETH in order to operate its proof-of-stake network.
This also removed a significant portion of the ETH supply from circulation, effectively making it as scarce as Bitcoin.
According to Konstantin Anissimov, executive director at CEX.IO, rising macro inflation benefits Ether just as much as it benefits Bitcoin.
He continues by predicting that the ETH/USD exchange rate will reach $3,000 based on an anti-inflation narrative.
„As things stand, the Federal Reserve has increased the size of its balance sheet from early 2020 to over $8 trillion—a substantial rise,“ he explained, adding:
„The reduced pricing is an avenue for market investors to accumulate the coins at a discount while trusting in their abilities to serve as the right hedge against the inherent inflation.“
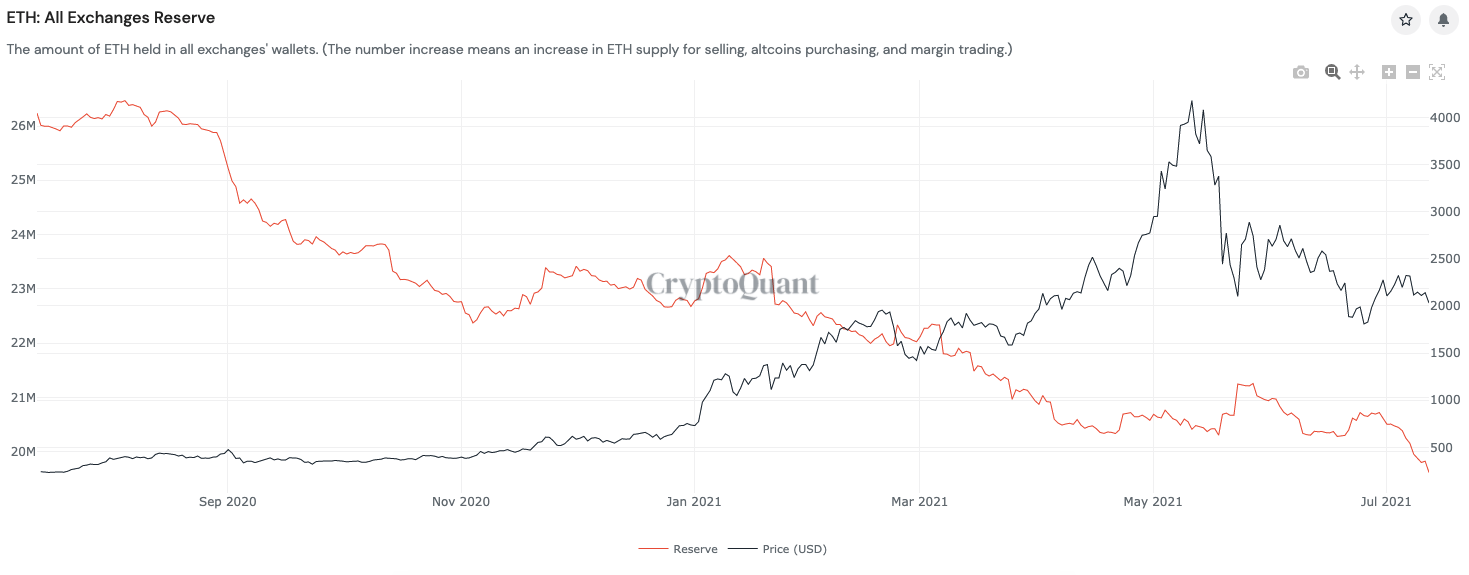
And so it appears, Ether accumulation is happening at a rapid pace. According to CryptoQuant, a South Korea-based blockchain analytics firm, the total ETH reserves across all the crypto exchanges have dropped by more than half in the wake of its Q2/2021 price correction from $4,384-top to $1,700-low.
Correlation risks
The correlation between Ether and Bitcoin continues to be a bottleneck as ETH targets new highs.
Nonetheless, Josh Arnold, a financial analyst with Seeking Alpha, pointed out that Ether and Bitcoin can be negatively correlated at times.
A correlation efficiency of 0.64 is not ideal.
Arnold instead focused on Ether’s price chart structure, noting that the cryptocurrency topped out in mid-May 2021 and formed a descending triangle pattern.
After a brief period of consolidation, descending triangles are typically continuation patterns that point prices in the direction of their previous trends.
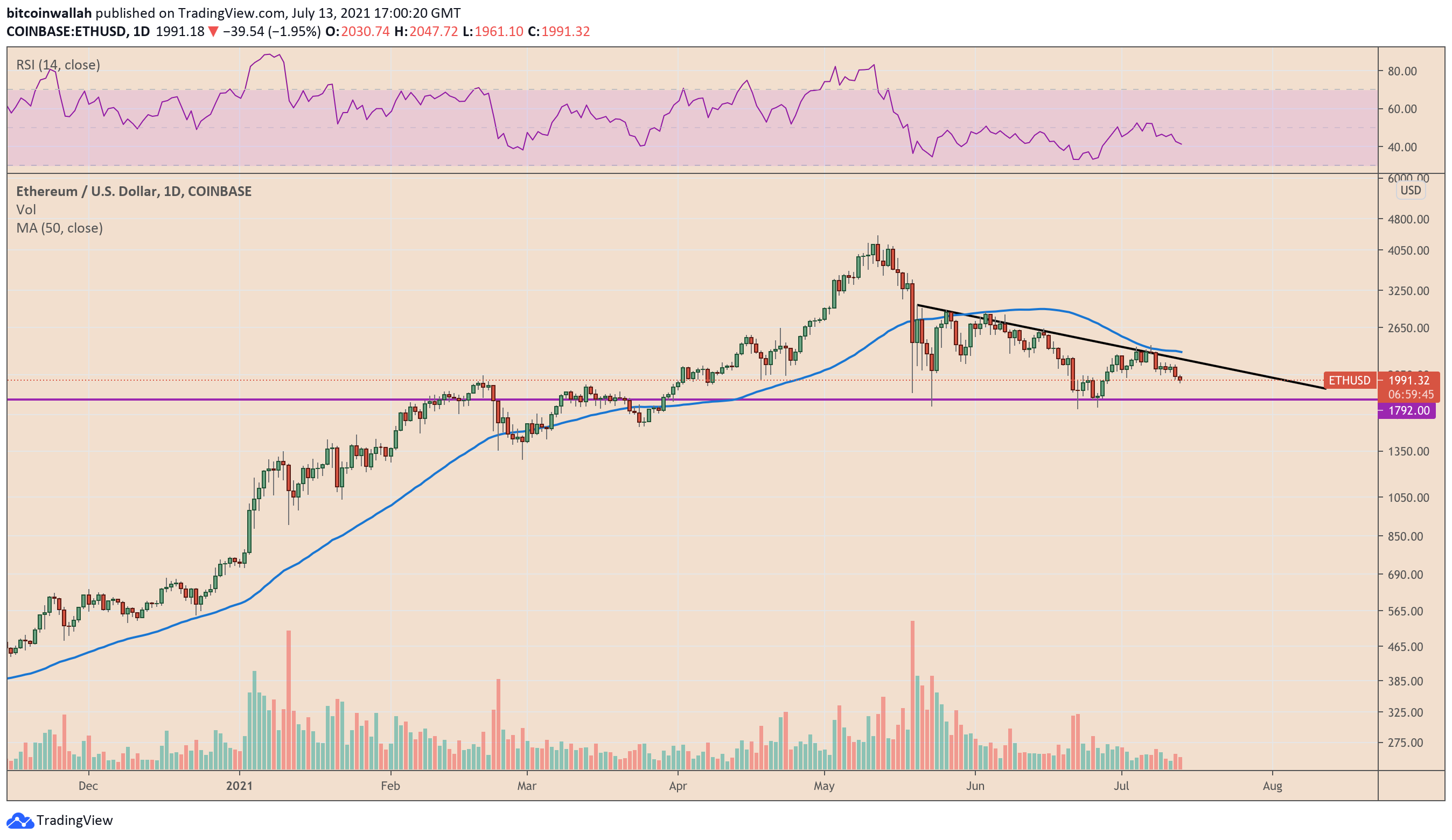
Arnold noted that Ether bulls need to hold Triangle support to maintain their upside bias or they would risk losing the market to bears. He explained:
„A descending triangle break to the downside would see Ethereum plumb new 2021 lows and try to find support again, but at much lower levels.“
But given Ether’s resilience against bears, Arnold anticipated that the cryptocurrency might end up rising higher.
The views and opinions expressed here are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of CoinNewsDaily. Every investment and trading move involves risk, you should conduct your own research when making a decision.























