
What is Algorand?
One of the founders of Algorand is Silvio Micali, an MIT professor who won the Turing Award for his work in cryptography. He made the network in 2017.
Algorand is a permissionless blockchain protocol that anyone can use to make apps and move money.
The Algorand protocol is based on a new consensus algorithm that allows for fast, safe, and scalable transactions.
Algorand solves the problems that most older blockchains have, especially when it comes to scalability and consensus.
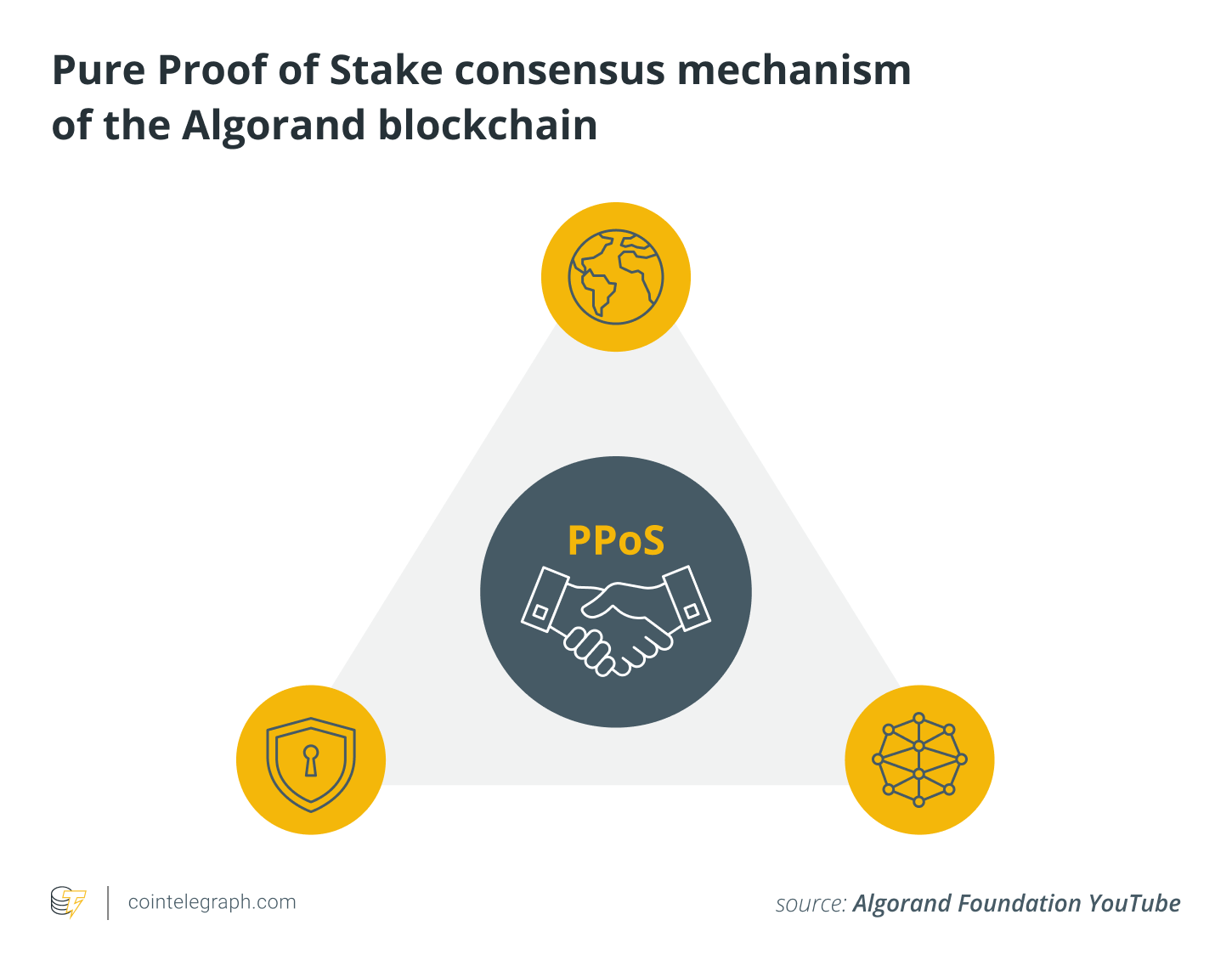
Pure proof-of-stake (PPoS) is the consensus protocol used on the blockchain. It chooses validators at random based on the weight of their stake in ALGO coins.
What is Algorand trying to solve?
Security, scalability, and decentralization are three of the biggest problems that most blockchains have. The Algorand protocol is designed to solve all three of these problems.
A group of people call this the „blockchain trilemma.“ The Algorand network says it can solve the following three problems:
Security
This means that the Algorand protocol is safe from malicious attacks, making it ideal for transactions, holding high-value assets, and building secure business applications.
It protects both the network and the consensus protocol. It also protects individual users‘ accounts.
Scalability
The Algorand protocol can handle a lot of transactions per second, which makes it a better solution than Bitcoin or Ethereum because it can handle more transactions per second.
Algorand’s consensus protocol doesn’t need the same amount of computing power as Bitcoin to solve cryptographic problems, so it doesn’t use as much.
Instead, the cost of the protocol’s computation per user is only used to make and check signatures, as well as simple counting operations.
According to Algorand, it can „scale to millions of users and keep a high transaction rate without putting a lot of money into the pockets of the people who use it.“
Decentralization
Algorand is completely decentralized, with no single authority or single point of control.
Transactions are checked by other nodes in the network, and each node has an equal say in the decisions that are made.
This makes Algorand a system that doesn’t have a lot of power.
The committee that decides whether or not a block should be added to the network is made up of people who are both random and anonymous. This means that everyone on the network has a chance of being part of the committee.
There isn’t a set committee, and the people who run its nodes come from all over the world.
How does Algorand work?
This is what makes Algorand different from other blockchains: It uses the PPoS consensus algorithm. This algorithm uses a Byzantine agreement protocol to make sure everyone agrees.
If one of the nodes in the network was hacked, the native token ALGO would be protected with unique keys. This would happen automatically.
Bitcoin’s consensus mechanism, proof-of-work (PoW), takes a lot of energy and computing power to make and check new blocks.
PPoS, on the other hand, makes it easier and faster to make and validate new blocks.
In this case, ALGO holders are chosen at random to check and approve each block in the chain.
In each new block, a new group, or committee, is chosen to work on the project.
Through the PPoS protocol, only people who own a lot of ALGO could be able to do things that could harm other people’s security.
However, because the system is based on codependency, people who do bad things would also hurt their ALGO.
As a result, any majority owner would not be happy with this kind of bad behavior.

In one second, Algorand can do 1,000 transactions, and all of them will be final and done right away.
Algorand also has a fixed supply of 10 billion tokens to make the network more stable.
There are a lot of these tokens locked up and haven’t been given out yet.
Algorand protocol structure
The Algorand protocol is built on three fundamental concepts:
- Transactions: Transactions are the basic unit of account in the Algorand network. They are used to transfer value and are verified by all participating nodes in the network.
- Blocks: Blocks are groups of transactions collected into a single unit and verified by the consensus algorithm.
- Consensus: The consensus algorithm is responsible for verifying blocks and ensuring that they meet the requirements of the Algorand protocol. It also rewards users who participate in its operation.
Algorand staking mechanism: Pure proof-of-stake
PPoS is how Algorand’s system works. The more tokens a user has in the system, or „stake,“ the more influence they have on which block is chosen, or how big the block will be.
Each user has a chance to be chosen, and the weight of their proposals and votes is based on how much money they have.
Users are chosen at random and kept secret so that they can propose and vote on blocks.
This way, the network’s security is linked to how honest most of its users are in its economy.
In the long run, if most of the money is in honest hands, the system will stay safe.
This is in contrast to other consensus mechanisms like PoW, DPoS, and BPoS, which make small groups in the economy responsible for the whole system’s safety.
The idea is that a small group of people can stop other people from using these methods.
Algorand’s method makes it almost impossible for people who have smaller stakes in the system to hurt the whole network.
As a result, majority owners would also not be able to act maliciously, because doing so would make their own assets less valuable and make the currency less valuable.
Algorand block production under PPoS
Under Algorand’s PPoS system, new blocks are built in two stages.
First, a single token is chosen at random during the first phase of the game.
The person who owns this token is in charge of coming up with the next block.
1000 tokens are chosen at random from the rest of the tokens that are in the system. This is the second phase.
Members of the phase-2 committee own these tokens, and they are in charge of making sure the block that was proposed in phase 1 is OK.
If a committee member is chosen again, it’s possible for them to be chosen more than once.
People in the committee will also vote more than once when they agree on the next block.
The second phase of Algorand’s block-making process was put in place to fight any bad actors.
Bad people who want to harm the network will be outvoted by the majority, so they’ll act in line with the rules for the good of everyone else.
Algorand’s native cryptocurrency: ALGO
People who live on the Algorand network use a currency called ALGO.
ALGO tokens are used to pay transaction fees and reward users who help the network come to a consensus, which is how the network works.
You can make transactions with ALGO quickly, no matter how many you make in a day. It doesn’t matter how many transactions you make.
Transaction fees are also very low.
Unlike Ethereum, which charges a lot of gas fees for transactions, Algo transactions cost very little to make and take place.

How can I buy ALGO cryptocurrency?
There are a lot of ways to buy ALGO.
In the same way you would buy any other cryptocurrency, you can buy it from another person in person or over the internet.
Instead, you could look for a crypto ATM near you that sells ALGO.
Crypto ATM rates can be very high, and there’s no way to know if you’ll be able to find someone who will trade with you.
If you want a simple way to buy ALGO, you can buy it on a cryptocurrency exchange.
Some of the most popular exchanges that offer ALGO are Binance, Kraken, and Coinbase.
Credit or debit cards are used to buy ALGO on these exchanges so that you can buy it.
People who want to do this first need to get a crypto wallet that can hold the ALGO coins.
Some wallets that work with ALGO are Pera Wallet, My Algo, Coinbase, and Ledger, to name a few.

To fill your wallet now that you’ve set up your wallet, find an exchange that can accept ALGO.

If you don’t already have an account on the exchange, set one up. Then, get it checked out.
To start your trade, choose „Algorand“ from the list of things to buy or sell.
Input the amount of money you want to buy ALGO coins with and then check out your purchase before you click „submit.“























